Examples of endangered species tell us about the habitat. In a world where biodiversity is increasingly threatened by human activities, the plight of endangered species is a matter of growing concern. These species, on the brink of extinction, require urgent attention and conservation efforts. In this article, we’ll explore examples of endangered species from various ecosystems, highlighting their unique aspects and the challenges they face.
What are Endangered Species?
Endangered species are organisms that are at risk of extinction due to various factors such as habitat loss, poaching, climate change, and pollution. To raise awareness and prioritize conservation efforts, it’s crucial to highlight some emblematic examples of these endangered species.
Terrestrial Endangered Species
Pangolin
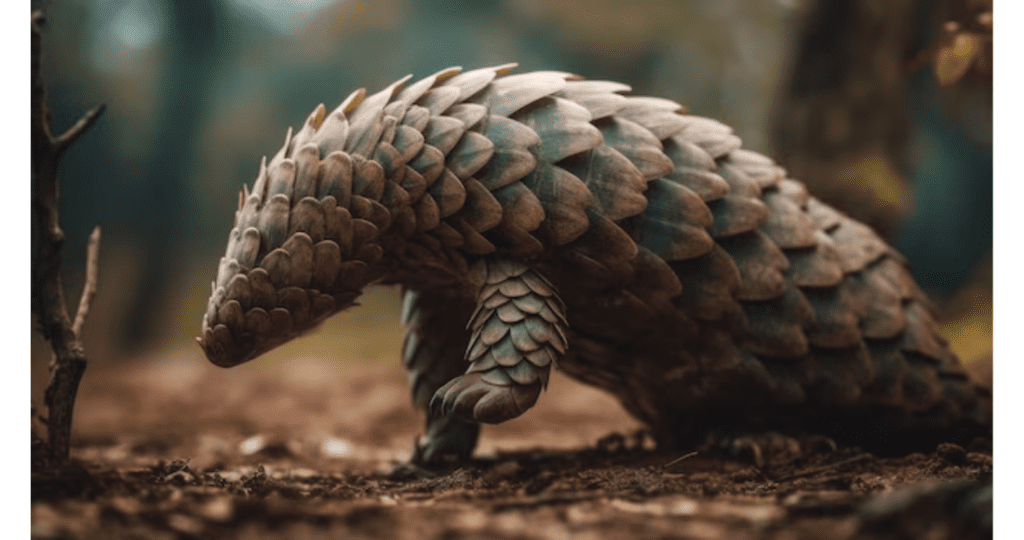

- Scientific Name: Manis spp.
- Habitat: Asia and Africa.
- Unique Aspect: Pangolins are the only mammals covered in protective scales made of keratin. They are also known for their unique tongue, longer than their body, used for catching insects.
- Challenges: Illegal wildlife trade, primarily driven by the demand for their scales and meat, poses a severe threat to pangolins.
Sumatran Tiger
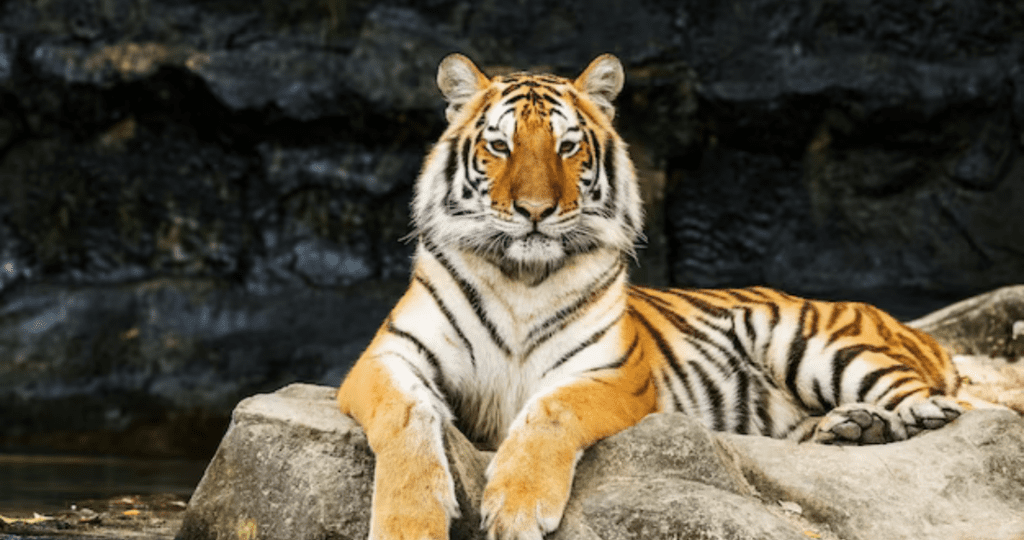

- Scientific Name: Panthera tigris sumatrae.
- Habitat: Sumatra, Indonesia.
- Unique Aspect: The Sumatran tiger is the smallest of all tiger subspecies, characterized by its darker fur and thick stripes.
- Challenges: Habitat loss due to deforestation and poaching for their body parts and bones, driven by the illegal wildlife trade.
Mountain Gorilla
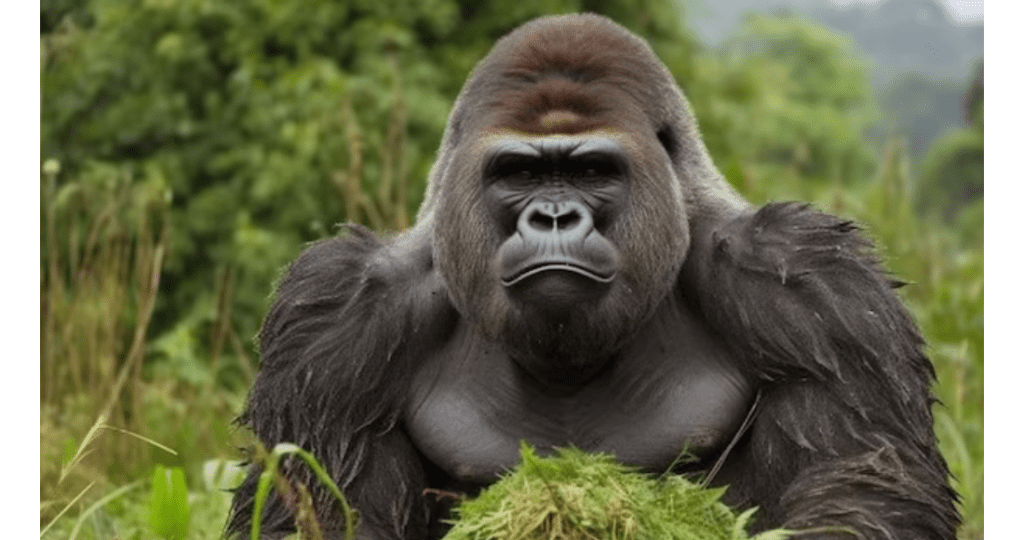

- Scientific Name: Gorilla beringei beringei.
- Habitat: Volcanic mountains in Central and East Africa.
- Unique Aspect: These gentle giants are known for their complex social structures and remarkable strength.
- Challenges: Habitat destruction, civil conflict, and poaching for the illegal wildlife trade have reduced their numbers significantly.
Aquatic Endangered Species
Vaquita

- Scientific Name: Phocoena sinus.
- Habitat: Gulf of California, Mexico.
- Unique Aspect: The vaquita is the world’s smallest and most endangered porpoise species.
- Challenges: Bycatch in gillnets used for illegal fishing practices is the primary threat to their survival.
Sea Turtle

- Scientific Name: Various species (e.g., Chelonia mydas, Dermochelys coriacea).
- Habitat: Oceans worldwide.
- Unique Aspect: Sea turtles have distinctive shells, and they are known for their incredible long-distance migrations.
- Challenges: Habitat destruction, pollution, and bycatch in fishing gear are major threats to sea turtles.
Blue Whale
- Scientific Name: Balaenoptera musculus.
- Habitat: Oceans globally.
- Unique Aspect: Blue whales are the largest animals to have ever lived on Earth, with hearts as big as small cars.
- Challenges: Collisions with large vessels and climate change-induced shifts in prey availability threaten their populations.
Avian Endangered Species
Kakapo

- Scientific Name: Strigops habroptilus.
- Habitat: New Zealand.
- Unique Aspect: The kakapo, also known as the night parrot, is a flightless, nocturnal parrot.
- Challenges: Predation by introduced species and habitat destruction have pushed them to the brink of extinction.
California Condor
- Scientific Name: Gymnogyps californianus.
- Habitat: Western United States.
- Unique Aspect: The California condor is one of the world’s rarest bird species and has a wingspan of nearly 10 feet.
- Challenges: Lead poisoning from ingesting spent lead ammunition and habitat degradation are significant threats.
Philippine Eagle

- Scientific Name: Pithecophaga jefferyi.
- Habitat: Philippines.
- Unique Aspect: Known as the “Monkey-eating Eagle,” it is one of the largest and most powerful eagles globally, preying on monkeys and other large prey.
- Challenges: Deforestation and hunting have severely reduced their population.
The examples provided here are just a snapshot of the many endangered species facing the threat of extinction. Humanity must take collective action to protect these remarkable creatures and their habitats. Conservation efforts, stricter wildlife protection laws, and global awareness are essential steps toward ensuring a future where these species can thrive once again.
25 Examples of Endangered Species
In a world facing unprecedented environmental challenges, the preservation of endangered species is of paramount importance. These creatures play a crucial role in our ecosystems and reflect the rich tapestry of life on Earth. In this article, we’ll explore 25 examples of endangered species from various corners of the globe, each with its unique characteristics and the factors threatening its existence.
| Species | Habitat | Population | Threats |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Amur Leopard | Russian Far East, China | Approx. 100 | Habitat loss, poaching |
| 2. Sumatran Elephant | Sumatra, Indonesia | Approx. 2,400 | Deforestation, habitat fragmentation, human-wildlife conflict |
| 3. Giant Panda | China | Approx. 1,800 | Habitat loss, low reproductive rate |
| 4. Javan Rhino | Java, Indonesia | Approx. 72 | Habitat loss, poaching |
| 5. Vaquita | Gulf of California, Mexico | Approx. 10 | Bycatch in fishing nets, illegal wildlife trade |
| 6. Black Rhinoceros | Africa | Approx. 5,500 | Poaching for their horns |
| 7. Kakapo | New Zealand | Approx. 213 | Predation by introduced species, habitat loss |
| 8. Saola | Vietnam, Laos | Unknown | Habitat loss, hunting |
| 9. Philippine Eagle | Philippines | Approx. 400 | Deforestation, hunting |
| 10. Iberian Lynx | Spain, Portugal | Approx. 400 | Habitat loss, declining prey availability |
| 11. Western Lowland Gorilla | Central Africa | Approx. 100,000 | Poaching, habitat loss |
| 12. Northern Right Whale | North Atlantic | Approx. 400 | Ship strikes, entanglement in fishing gear |
| 13. Bengal Tiger | India, Bangladesh | Approx. 2,500 | Poaching, habitat fragmentation |
| 14. Blue Whale | Oceans worldwide | Estimated 10,000-25,000 | Ship strikes, climate change, noise pollution |
| 15. Cross River Gorilla | Nigeria, Cameroon | Approx. 200 | Poaching, habitat loss |
| 16. Mountain Gorilla | Central Africa | Approx. 1,000 | Poaching, habitat loss, civil unrest |
| 17. Leatherback Sea Turtle | Global | Unknown | Plastic pollution, habitat loss, bycatch in fishing nets |
| 18. Snow Leopard | Central and South Asia | Approx. 4,000 | Poaching, habitat loss, retaliatory killing by herders |
| 19. Hawksbill Sea Turtle | Global | Unknown | Illegal trade in shells, habitat degradation |
| 20. African Wild Dog | Africa | Approx. 6,600 | Habitat loss, human-wildlife conflict, disease |
| 21. Bornean Orangutan | Borneo | Approx. 104,700 | Deforestation, palm oil production, illegal pet trade |
| 22. Red Wolf | United States | Approx. 20-25 | Habitat loss, hybridization with coyotes, poaching |
| 23. Pygmy Three-Toed Sloth | Isla Escudo de Veraguas, Panama | Approx. 79 | Habitat loss, human disturbance, climate change |
| 24. Chinese Pangolin | Asia, Africa | Unknown | Illegal trade in scales and meat, habitat loss |
| 25. African Penguin | Southern Africa | Approx. 25,000 | Overfishing, oil spills, habitat destruction |
These species represent just a fraction of the many animals and plants facing the risk of extinction. The causes of endangerment vary from habitat destruction and pollution to poaching and climate change. Conservation efforts, such as habitat preservation, anti-poaching measures, and public awareness campaigns, are essential to protect these species and ensure a biodiverse future for our planet.
By learning about these endangered species and supporting conservation organizations, we can contribute to their survival and help preserve the Earth’s incredible biodiversity for generations to come. Let’s work together to protect these remarkable creatures and the ecosystems they call home.

