When it comes to understanding the principles of mechanics and simple machines, levers play a crucial role. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of 3rd class levers examples, exploring their functions, applications, and real-life instances.
Understanding 3rd Class Levers
Definition of 3rd Class Lever
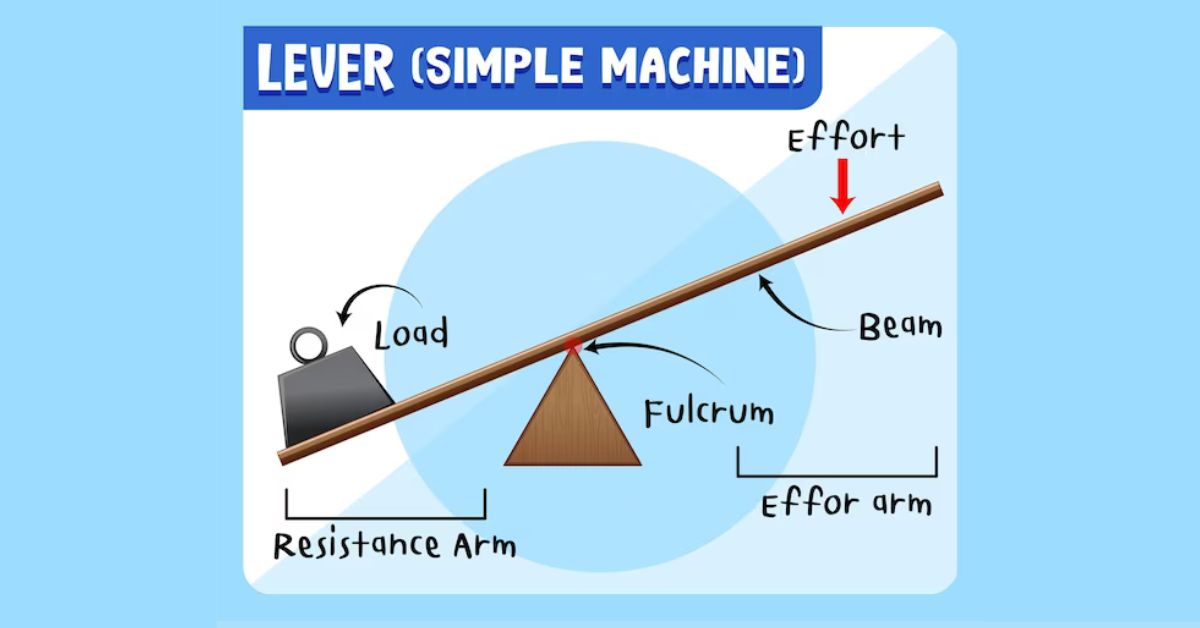
A lever is a basic mechanical device consisting of a rigid bar pivoted at a fixed point, known as the fulcrum. 3rd Class levers are characterized by having the effort applied between the fulcrum and the load, making them unique in their mechanical advantage.
Components of 3rd class lever
- Fulcrum: The fixed point on which the lever rotates.
- Effort: The force applied to move the lever.
- Load: The resistance or object being moved.
Real-Life Examples of 3rd-Class Levers
Examples of 3rd class lever are given below;
- Human Arm: The forearm serves as the lever, with the elbow acting as the fulcrum, the bicep providing effort, and the hand holding an object as the load.
- Fishing Rod: The hand holding the rod serves as the fulcrum, the effort comes from the angler’s muscles, and the load is the tension in the fishing line.
- Tweezers: The pivot point acts as the fulcrum, the fingers exert effort, and the load is the object being gripped.
- Baseball Bat Swing: When a batter swings a baseball bat, the hands act as the effort, the fulcrum is where the hands grip the bat, and the load is the weight of the bat.
- Nutcracker: The hinge serves as the fulcrum, the effort is applied by squeezing the handles, and the load is the nut being cracked.
- Scissors: The screw joint acts as the fulcrum, the effort is applied to the handles, and the load is the material being cut.
- Hockey Stick Shot: The hands on the stick serve as the effort, the fulcrum is where the hands grip the stick, and the load is the force applied to the puck.
- Pliers: The joint where the handles meet serves as the fulcrum, the effort is applied to the handles, and the load is the material being gripped.
- Broom Sweeping: The hands on the broom handle act as the effort, the fulcrum is where the hands grip the handle, and the load is the force applied to the broom.
- Shovel Use: The hands on the shovel handle serve as the effort, the fulcrum is where the hands grip the handle, and the load is the force applied to move the soil.
- Golf Club Swing: The hands on the golf club act as the effort, the fulcrum is where the hands grip the club, and the load is the force applied to the golf ball.
- Forceps: Used in medical procedures, forceps operate as 3rd class levers with the pivot point as the fulcrum, the effort applied by the user, and the load being the tissue or object being handled.
- Chopsticks: The hand holding the chopsticks acts as the fulcrum, the effort is applied by the fingers, and the load is the food being picked up.
- Nail Clippers: The pivot point on the clippers acts as the fulcrum, the effort is applied by squeezing the handles, and the load is the nail being cut.
- Hammering a Nail: The hands on the hammer handle serve as the effort, the fulcrum is where the hands grip the handle, and the load is the force applied to the nail.
- Cricket Bat Shot: The hands on the cricket bat act as the effort, the fulcrum is where the hands grip the bat, and the load is the force applied to the cricket ball.
- Rowing a Boat: The hands on the oar act as the effort, the fulcrum is where the hands grip the oar, and the load is the force applied to propel the boat.
- Nut Wrench: The pivot point on the wrench serves as the fulcrum, the effort is applied by turning the handle, and the load is the force applied to loosen or tighten the nut.
- Paint Roller Application: The hands on the roller handle act as the effort, the fulcrum is where the hands grip the handle, and the load is the force applied to the roller for painting.
- Lawnmower Operation: The hands on the lawnmower handle serve as the effort, the fulcrum is where the hands grip the handle, and the load is the force applied to push or maneuver the lawnmower.
Advantages and Applications of 3rd Class Lever
Precision and Control:
- Advantage: 3rd class levers provide a high level of precision and control in movements due to the effort being between the fulcrum and the load.
- Application: This advantage is crucial in activities such as surgery, where delicate and precise movements are required.
Enhanced Range of Motion:
- Advantage: The arrangement of components in 3rd class levers allows for an extended range of motion, making them suitable for tasks that demand flexibility.
- Application: Sports equipment like golf clubs or tennis rackets benefit from this enhanced range, enabling players to achieve optimal performance.
Reduced Effort for Speed:
- Advantage: 3rd class levers are effective in reducing the effort required for high-speed movements, making them ideal for activities demanding quick and agile responses.
- Application: In activities like throwing a ball, the design of the lever minimizes effort while maximizing the speed of the thrown object.
Tool Design and Manipulation:
- Advantage: Many hand tools, including pliers, forceps, and scissors, utilize the 3rd class lever configuration for efficient manipulation and control.
- Application: Craftsmen and surgeons benefit from the ease of use and precise control offered by tools designed as 3rd class levers.
Improved Force Application in Sports:
- Advantage: 3rd class levers are commonly found in sports equipment, such as hockey sticks, allowing athletes to efficiently apply force for powerful and controlled movements.
- Application: Athletes leverage this advantage in sports like hockey, lacrosse, and baseball, enhancing their ability to handle equipment with accuracy.
Efficient Body Movements:
- Advantage: The human body itself employs 3rd class levers in the musculoskeletal system, enabling efficient and controlled movements.
- Application: Everyday activities like picking up objects, writing, and using tools benefit from the biomechanical advantages provided by 3rd class levers in the human body.
Fine Motor Skills Development:
- Advantage: 3rd class levers contribute to the development of fine motor skills due to the intricate and controlled movements they enable.
- Application: Educational toys and tools designed with 3rd class lever principles aid in the development of fine motor skills in children.
Adaptability in Tool Design:
- Advantage: The versatility of 3rd class levers allows for various applications in tool design, adapting to specific tasks and requirements.
- Application: From simple hand tools to complex machinery, the adaptability of 3rd class levers finds application in a wide range of industrial and domestic tools.
Understanding the advantages and applications of 3rd class levers not only sheds light on their importance in mechanics but also highlights their diverse roles in everyday activities, sports, and specialized fields. Whether in the intricate movements of surgical procedures or the swift actions of a sports player, the unique characteristics of 3rd class levers contribute significantly to efficiency and precision.