Alpha blockers are a class of medications commonly used in the treatment of hypertension, also known as high blood pressure. With various options available, understanding the different Examples of Alpha Blockers For Hypertension and their effectiveness is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike.
Definition of Alpha Blockers
Alpha blockers are medications that work by blocking alpha receptors in blood vessels, leading to vasodilation and reduced blood pressure. They are often prescribed as part of a comprehensive treatment plan for hypertension.
Purpose of Alpha Blockers in Treating Hypertension
The primary goal of using alpha blockers in hypertension management is to relax blood vessels, allowing blood to flow more easily and lowering blood pressure levels.
Importance of Identifying Different Examples of Alpha Blockers
Identifying different examples of alpha blockers is essential for tailoring treatment plans to individual patient needs. Each medication has its unique characteristics and considerations, and understanding these differences helps optimize treatment outcomes.
Alpha Blockers for Hypertension: Overview
Brief Explanation of Hypertension
Hypertension is a common condition characterized by elevated blood pressure levels. Left untreated, it can increase the risk of serious health complications such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage.
Mechanism of Action of Alpha Blockers in Treating Hypertension
Alpha blockers block alpha receptors in blood vessels, leading to vasodilation and decreased peripheral vascular resistance. This results in lowered blood pressure levels.
General Considerations Before Using Alpha Blockers for Hypertension
Before prescribing alpha blockers for hypertension, healthcare providers will consider factors such as the patient’s medical history, other medications they may be taking, and any potential drug interactions.
10 Examples of Alpha Blockers for Hypertension
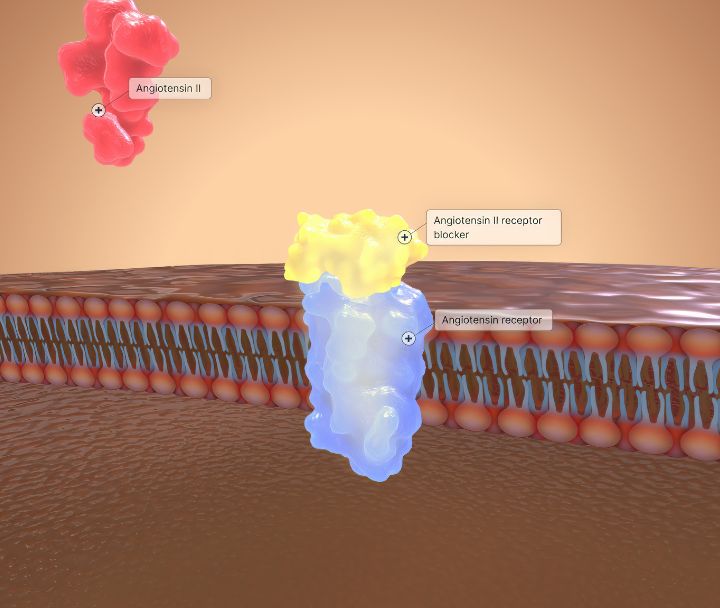
Here are 10 examples of alpha blockers for hypertension;
1. Doxazosin (Cardura)
- Dosage: Typically started at 1 mg daily and titrated up to 8 mg daily.
- Side Effects: Common side effects include dizziness, fatigue, and headache.
- Effectiveness: Doxazosin helps lower blood pressure by relaxing blood vessels, allowing for easier blood flow.
2. Prazosin (Minipress)
- Dosage: Initial dose usually starts at 1 mg, with gradual titration.
- Side Effects: Potential side effects include dizziness, drowsiness, and weakness.
- Effectiveness: Prazosin works by blocking alpha receptors in blood vessels, leading to vasodilation and decreased blood pressure.
3. Terazosin (Hytrin)
- Dosage: Initial dose ranges from 1 mg to 5 mg once daily, with gradual titration.
- Side Effects: Common side effects include dizziness, headache, and fluid retention.
- Effectiveness: Terazosin relaxes blood vessels, allowing blood to flow more easily and reducing blood pressure.
4. Alfuzosin (Uroxatral)
- Dosage: Usually taken as 10 mg once daily with food.
- Side Effects: Common side effects may include dizziness, headache, and fatigue.
- Effectiveness: Alfuzosin helps lower blood pressure by relaxing smooth muscles in the blood vessels, leading to vasodilation.
5. Tamsulosin (Flomax)
- Dosage: Typically prescribed as 0.4 mg once daily.
- Side Effects: Common side effects include dizziness, headache, and retrograde ejaculation.
- Effectiveness: Tamsulosin works by relaxing muscles in the prostate and bladder neck, as well as blood vessels, leading to reduced blood pressure.
6. Silodosin (Rapaflo)
- Dosage: Typically prescribed as 8 mg once daily with a meal.
- Side Effects: Common side effects include dizziness, diarrhea, and retrograde ejaculation.
- Effectiveness: Silodosin has shown efficacy in reducing blood pressure levels by relaxing smooth muscles in the blood vessels.
7. Bunazosin (Nebilet)
- Dosage: Dosage ranges from 0.5 mg to 4 mg once daily, depending on the patient’s response.
- Side Effects: Common side effects include dizziness, headache, and palpitations.
- Effectiveness: Bunazosin’s alpha-blocking effects contribute to vasodilation and decreased blood pressure levels.
8. Naftopidil (Flivas)
- Dosage: Typically prescribed as 25 mg once daily.
- Side Effects: Common side effects include dizziness, headache, and nasal congestion.
- Effectiveness: Naftopidil helps lower blood pressure by blocking alpha receptors in blood vessels, leading to vasodilation.
9. Indoramin (Baratol)
- Dosage: Dosage typically ranges from 25 mg to 200 mg daily, divided into multiple doses.
- Side Effects: Possible side effects include dizziness, drowsiness, and dry mouth.
- Effectiveness: Indoramin’s alpha-blocking effects contribute to the relaxation of blood vessels and decreased blood pressure.
10. Phentolamine (Regitine)
- Dosage: Dosage varies depending on the indication and route of administration.
- Side Effects: Side effects may include hypotension, tachycardia, and flushing.
- Effectiveness: Phentolamine blocks alpha receptors in blood vessels, leading to vasodilation and reduced blood pressure levels.
These examples highlight the range of alpha blockers available for the treatment of hypertension. Each medication has its dosage, side effects, and effectiveness profile, and the choice of alpha blocker depends on factors such as the patient’s medical history and individual response to treatment.

