Alpha blockers are a class of medications commonly used in the treatment of various conditions, including kidney stones. Understanding the different examples of alpha blockers for kidney stones and their effectiveness in managing kidney stones is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike.
Definition of Alpha Blockers
Alpha blockers are medications that work by relaxing the muscles in certain parts of the body, including the urinary tract. By doing so, they can help improve urine flow and alleviate symptoms associated with conditions such as kidney stones.
Purpose of Alpha Blockers in Treating Kidney Stones
The primary purpose of alpha blockers in treating kidney stones is to facilitate the passage of stones through the urinary tract.
- Alpha blockers work by relaxing the smooth muscles in the ureter, which is the tube that connects the kidneys to the bladder.
- By doing so, alpha blockers help widen the ureter and ease the movement of kidney stones, thereby reducing pain and discomfort for the patient.
- Additionally, alpha blockers may help decrease ureteral spasm, allowing for smoother stone passage and potentially reducing the need for surgical intervention.
- Overall, the goal of using alpha blockers in kidney stone treatment is to promote natural stone expulsion and alleviate associated symptoms.
Importance of Identifying Different Types of Alpha Blockers
The importance of identifying different examples of alpha blockers lies in the diverse characteristics and effectiveness of each medication in treating kidney stones.
- Understanding the range of available options allows healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans to individual patient needs, taking into account factors such as side effects, dosage regimens, and potential drug interactions.
- This personalized approach helps optimize treatment outcomes, improve patient satisfaction, and minimize adverse effects, ultimately enhancing the overall quality of care for individuals with kidney stones.
Alpha Blockers for Kidney Stones: Overview
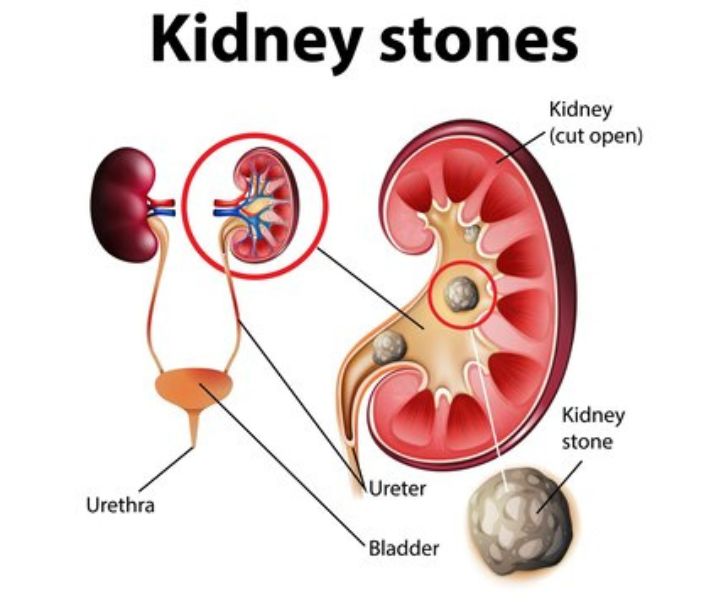
Brief Explanation of Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are small, hard deposits that form in the kidneys and can cause intense pain when they pass through the urinary tract. Alpha blockers are often prescribed to help relax the muscles in the ureter, making it easier for the stones to pass.
Mechanism of Action of Alpha Blockers in Treating Kidney Stones
Alpha blockers work by blocking alpha receptors in the smooth muscle of the urinary tract, leading to the relaxation of the muscles and increased urine flow. This helps facilitate the passage of kidney stones through the ureter.
General Considerations Before Using Alpha Blockers for Kidney Stones
Before prescribing alpha blockers for kidney stones, healthcare providers will consider factors such as the size and location of the stones, the patient’s medical history, and any potential drug interactions.
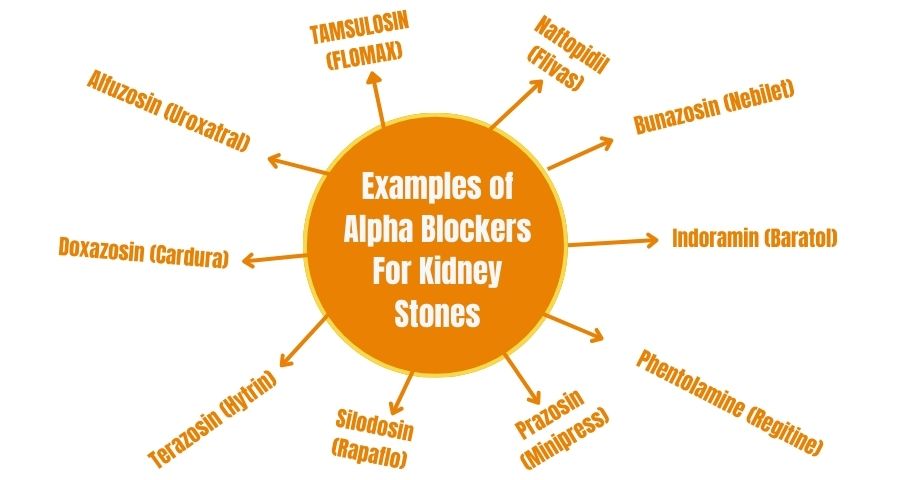
Examples of Alpha Blockers for Kidney Stones

Here are 10 examples of alpha blockers for kidney stones,
1. Tamsulosin (Flomax)
- Dosage: Typically prescribed as 0.4 mg once daily
- Side Effects: Common side effects include dizziness, headache, and retrograde ejaculation
- Effectiveness: Clinical studies have shown tamsulosin to increase the likelihood of spontaneous stone passage and reduce the need for surgical intervention.
2. Alfuzosin (Uroxatral)
- Dosage: Usually taken as 10 mg once daily with food
- Side Effects: Common side effects may include dizziness, headache, and fatigue
- Effectiveness: Alfuzosin has been found to improve stone passage rates and reduce the time to stone expulsion.
3. Doxazosin (Cardura)
- Dosage: Initial dose typically starts at 1 mg daily, with gradual titration
- Side Effects: Possible side effects include dizziness, fatigue, and nasal congestion
- Effectiveness: Doxazosin may help relax the ureteral muscles, facilitating stone passage in some patients.
4. Terazosin (Hytrin)
- Dosage: Initial dose ranges from 1 mg to 5 mg once daily, with gradual titration
- Side Effects: Common side effects include dizziness, headache, and fluid retention
- Effectiveness: Terazosin can aid in ureteral relaxation, potentially easing the passage of kidney stones.
5. Silodosin (Rapaflo)
- Dosage: Typically prescribed as 8 mg once daily with a meal
- Side Effects: Common side effects include dizziness, diarrhea, and retrograde ejaculation
- Effectiveness: Silodosin has shown efficacy in improving stone passage and reducing associated pain.
6. Prazosin (Minipress)
- Dosage: Initial dose usually starts at 1 mg, with gradual titration
- Side Effects: Potential side effects include dizziness, headache, and weakness
- Effectiveness: Prazosin may help relax the smooth muscles of the ureter, facilitating stone expulsion.
7. Phentolamine (Regitine)
- Dosage: Dosage varies depending on the indication and route of administration
- Side Effects: Side effects may include hypotension, tachycardia, and flushing
- Effectiveness: Phentolamine’s alpha-blocking properties may aid in ureteral relaxation, potentially assisting in stone passage.
8. Indoramin (Baratol)
- Dosage: Dosage typically ranges from 25 mg to 200 mg daily, divided into multiple doses
- Side Effects: Possible side effects include dizziness, drowsiness, and dry mouth
- Effectiveness: Indoramin’s alpha-blocking effects may contribute to the relaxation of ureteral muscles, facilitating stone expulsion.
9. Bunazosin (Nebilet)
- Dosage: Dosage ranges from 0.5 mg to 4 mg once daily, depending on the patient’s response
- Side Effects: Common side effects include dizziness, headache, and palpitations
- Effectiveness: Bunazosin’s alpha-blocking properties may assist in relieving ureteral spasms and promoting stone passage.
10. Naftopidil (Flivas)
- Dosage: Typically prescribed as 25 mg once daily
- Side Effects: Common side effects include dizziness, headache, and nasal congestion
- Effectiveness: Naftopidil’s alpha-blocking effects may help relax the ureter, facilitating the passage of kidney stones.
These examples provide a range of alpha blockers commonly used in the treatment of kidney stones, each with its dosage, side effects, and effectiveness profile. Patients need to discuss these options with their healthcare providers to determine the most suitable treatment approach for their individual needs.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Alpha Blocker for Kidney Stones
Patient’s Medical History
- Patients with certain medical conditions or taking specific medications may require adjustments in the choice or dosage of alpha blocker.
Allergies and Sensitivities
- Patients with known allergies or sensitivities to specific alpha blockers should inform their healthcare provider to avoid potential adverse reactions.
Potential Drug Interactions
- Alpha blockers may interact with other medications, including antihypertensives and erectile dysfunction drugs.
- Healthcare providers should review patients’ medication regimens to minimize the risk of drug interactions
Future Outlook for Alpha Blockers in Treating Kidney Stones
- Ongoing research and clinical trials continue to explore the efficacy and safety of alpha blockers in the management of kidney stones, promising advancements in treatment options for patients.